Scientific and Therapeutic Evidence of Hijama (Cupping Therapy)
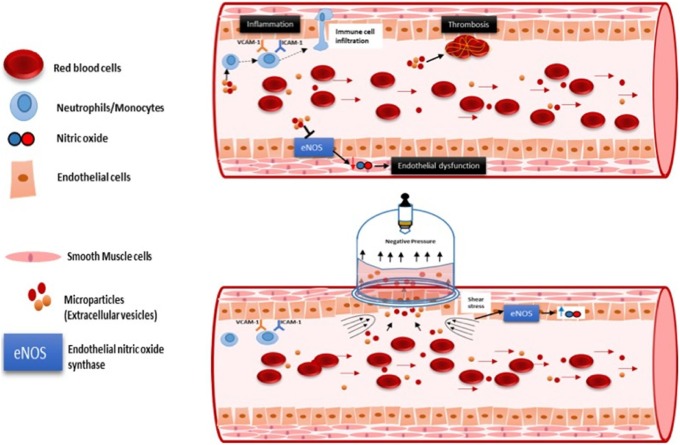
Hijama, also known as wet cupping, has long been used as a holistic healing method in traditional medicine. Today, growing scientific research supports its therapeutic effects on the neural, hematological, and immune systems. This article explores the evidence-backed mechanisms, clinical outcomes, and potential risks of Hijama therapy.
How Hijama Works: Scientific Insights
According to the American Journal of Chinese Medicine (Vol. 36, No. 1, p. 42), the mechanism of wet cupping affects multiple systems in the body:
Neural System Effects
- Regulation of neurotransmitters: Serotonin, dopamine, endorphins, CGRP, and acetylcholine
- Modulation of neuron membrane charges
Immune and Hematological System
- Activation of natural killer cells
- Enhanced detoxification and inflammatory response
- Stimulates blood circulation and improves cell signaling
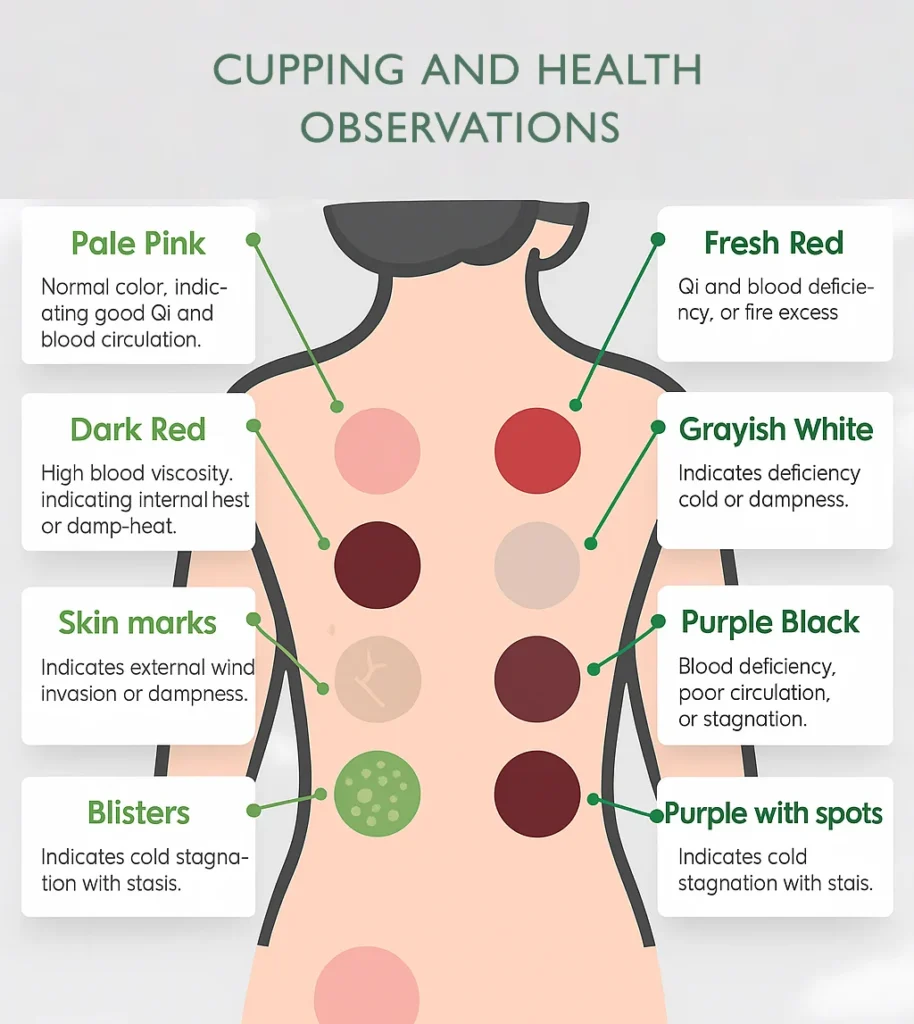
Therapeutic Evidence of Hijama
Non-Specific Blood Clearance
- Removes pathological substances from blood
- Beneficial for conditions like hyperlipidemia, hypertension, atherosclerosis
Pain Relief
- Significant improvements in rheumatoid arthritis, joint pain, and musculoskeletal issues
- Reduces pain intensity, tender joints, and swelling
Pharmacological Potentiation
- Enhances effects of conventional treatments
- Noted in cases of migraine and arthritis
Immune System Enhancement
- Increases leukocytosis and natural killer cells
- Boosts the body’s defense mechanisms
Scientific Evidence and Clinical Indicators
Studies have introduced indexes to measure the effects of Hijama therapy:
- Excretion Value (EV): Measures waste substances removed
- Purification Index (PI): Plasma detox percentage
- Pharmacological Potentiation Index (PPI): Drug-response enhancement
- Immunological Index (II): Degree of immune activation
- Clinical Therapeutic Index (CTI): Improvement in clinical symptoms
Conditions Treated with Hijama
Musculoskeletal Disorders
- Lumbar disc herniation, cervical spondylosis, fibrositis
- Effective for chronic pain, knee osteoarthritis, neck and back pain
Cardiovascular & Metabolic Health
- Hyperlipidemia: Decreases triglycerides, cholesterol, LDL
- Hypertension: Lowers blood pressure and improves ECG results
- Improved liver and kidney function: Reduces liver enzymes and creatinine
Autoimmune and Immune Disorders
- Beneficial in rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, herpes zoster
- Improves immune markers and reduces inflammation
Neurological & Migraine Relief
- A study showed a 66% reduction in migraine severity with wet cupping
- Cupping outperformed standard treatments in multiple trials
Acne & Psoriasis:
Dermatological Benefits
- Meta-analysis showed a 2.14x higher cure rate vs. medication
- Decreases inflammation and improves natural immunity
Respiratory and Gastrointestinal Support
- Helps in COPD, bronchitis, and sinusitis
- Effective in treating Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, and constipation
Male Health
Improvements in erectile dysfunction and prostate health
Scientific Theories Behind Hijama
Pain-Gate Theory
Stimulation from cupping activates large nerve fibers, which block pain signals to the brain.
Immune Modulation Theory
Cupping reduces pro-inflammatory markers and enhances immune responses by promoting healing substances.
Safety, Effectiveness, and Potential Side Effects
Safety and Effectiveness
- Most studies report positive outcomes with minimal side effects
- Safe when performed by trained professionals using sterilized tools
Potential Risks
- Temporary discomfort, bruises, or circular marks
- Minor scarring or pigmentation
- Risk of infection if hygiene protocols aren’t followed
- Burns (rare, from fire cupping)
- Use caution if you have blood clotting disorders or take blood thinners
Final Thoughts
Modern science continues to explore the benefits of Hijama therapy, revealing its potential in pain relief, immune regulation, and chronic condition management. While more studies are needed for full clinical adoption, the evidence so far confirms that Hijama is a valuable, non-pharmacological healing approach when practiced safely.





